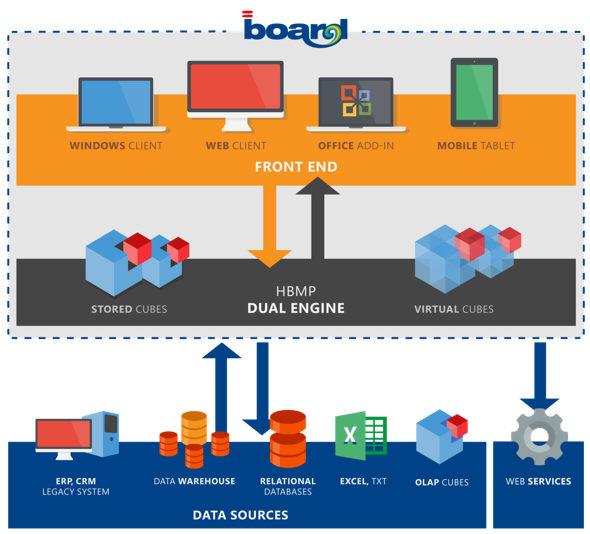
Board 7 architecture is based on the "Service Oriented Architecture" (SOA) paradigm. In this architecture you can identify a "service provider" which is the Board Server program, and a set of different service consumers which are the client programs, namely the Board 7 client, the MS-Office Add-ins and the Web browser client.

Board Client ,Board Web Client, Board Office Add-in and Board for Mobile are front-end user programs
Board Server is the multidimensional database engine that carries out all processing on the Board databases. It executes all aggregations, calculations, selections, procedures, data import procedures and any other interaction involving the Board multidimensional database. It also handles incoming connections from Board users. It performs user authentication, applies security restrictions or privileges and then dispatches user requests to different execution threads to carry out the multidimensional processing.
Board Database are the database files, located on a storage device. A Board database is a set of files stored in a directory. The Board database can be stored on the hard disk of the machine running the Board Server or on a storage device connected to it.
Communications between the client and the server uses a proprietary protocol named ROAR (Remote Object Access & Replication) which provides extremely high performance in communications and is designed to work efficiently over low bad-width connections such as WAN or the Internet. The ROAR protocol in Board 7 is built upon the Windows Communication Foundation (WCF) classes of Microsoft .Net Framework 3.5. It is a data convention format used in communications between the Board client and Board server programs.
The ROAR protocol transfers data from the client’s memory (Board Client) to the server’s memory (Board Server) through a compressed data stream. This technology is fundamentally more efficient compared to the verbose industry standards of XMLA and ODBO. The data traffic generated in the dialog between Board Client and Board Server is extremely low thanks to the specialized ROAR protocol, which has been designed for delivering performance over remote connections.